

Parkinson's & Dyskinesia
Clinical research
2025: For Parkinson's disease, a case series of using cannabinoids for the non-motor symptoms like cognitive impairment, insomnia & daytime sleepiness
Low Doses of Cannabis Extract Ameliorate Non-Motor Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease Patients: A Case Series
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/human-neuroscience/articles/10.3389/fnhum.2024.1466438/abstract
2025: In people with Parkinson's disease, 12 weeks of CBD improved working memory & with no adverse effects on other symptoms
Cannabidiol and cognitive functions/inflammatory markers in Parkinson's disease: A double-blind randomized controlled trial at Buriram Hospital (CBD-PD-BRH trial)
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1353802025005826
2025: In people with Parkinson's disease, those with decreased levels of CB1 receptors had more problems with gait, postural instability & rigidity
Impaired Gait, Postural Instability, and Rigidity in Relation to CB1 Receptor Availability in Parkinson's Disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39435606/
2024: For Parkinson's disease, two doctor’s advice on using cannabis
Advice to People with Parkinson's in My Clinic: Cannabis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38759024/
2024: In patients with Parkinson's disease, six months of treatment with nabilone (a synthetic mimic of THC) improved overall sleep, night time sleep problems & overall pain
Long-term safety and efficacy of open-label nabilone on sleep and pain in Parkinson´s Disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38491070/
2024: For Parkinson's disease, a case report on cannabis oil restoring mobility, appetite & mood
Cannabis oil in treating Parkinson’s disease: improvement of motor and non-motor symptoms: a case report
https://www.scielo.br/j/bjb/a/nqQFzz3NtnydWM8KWdfYyWz/
2024: In patients with Parkinson's disease, two weeks of a high CBD/low THC oil improved motor scores but perhaps worsened cognition & sleep
Short-Term Cannabidiol with Δ-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol in Parkinson's Disease: A Randomized Trial
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38487964/
2023: In patients with Parkinson's disorder, the majority using a 1:1 THC:CBD tincture saw an improvement in their cramping/dystonia, pain, spasticity, lack of appetite, dyskinesia & tremor while half lowered or stopped their opioid usage
Medical Cannabis in the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37191563/
2023: A clinical study found medical cannabis to be safe for Parkinson’s disease patients
Long-term safety of medical cannabis in Parkinson's disease: A retrospective case-control study
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37211456/
2023: A Parkinson’s clinical study focused on safety found formulas of THC/CBD to be well tolerated
A Phase Ib, Double Blind, Randomized Study of Cannabis Oil for Pain in Parkinson's Disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37476317/
2023: In a study of genes linked to Parkinson's disease, one of the results is the gene for the CB1 receptor
Genetic Insights into the Molecular Pathophysiology of Depression in Parkinson's Disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37374342/
2022: A survey of Parkinson’s patients finds that they use cannabis to help with improvements to motor function, sleep & pain
Cannabis use in Parkinson's disease-A nationwide online survey study
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35178701/
2022: In humans using medical cannabis, six months of use increased the coherence of their white matter while CBD reduced their mean diffusivity (higher water content in their brain, neuroprotective against demyelination diseases like Parkinson’s)
Increased White Matter Coherence Following Three and Six Months of Medical Cannabis Treatment
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36367574
2022: In patients with Parkinson’s disease using transcranial magnetic stimulation, the decrease in neuroinflammation seems to be mediated by increasing the level of CB2 receptors as well as increased levels of anandamide & 2-AG
High-Frequency Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation Regulates Astrocyte Activation by Modulating the Endocannabinoid System in Parkinson's Disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35672602
2022: In Parkinson’s patients, an eye-tracking study found that nabilone (a pharmaceutical THC analog) did not cause any negative effects on cognition
Eye Tracking in Patients with Parkinson's Disease Treated with Nabilone-Results of a Phase II, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group Pilot Study
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35625047
2022: In Parkinson’s patients, nabilone (a pharmaceutical THC analog) had beneficial effects on sleep outcomes
Effects of nabilone on sleep outcomes in patients with Parkinson's disease: a post-hoc analysis of NMS-Nab study
https://movementdisorders.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/mdc3.13471
2022: In patients with Parkinson’s disease, brain scans showed lower levels of CB1 receptors in several brain regions – and the medication that they used helped to increase CB1 receptors towards normal levels
Cannabinoid Receptor Type 1 in Parkinson's Disease: A Positron Emission Tomography Study with [ 18 F]FMPEP-d 2
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35674270
2022: In patients with Parkinson’s disease, they reported using more CBD products via oral administration for sleep, pain & mood
Higher Risk, Higher Reward? Self-Reported Effects of Real-World Cannabis Use in Parkinson's Disease
https://movementdisorders.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/mdc3.13414
2022: The Michael J Fox Foundation released the results of a survey on the use of cannabinoid products for Parkinson’s disease & they reported using more CBD products
Higher risk, higher reward? Self-reported effects of real-world cannabis use in Parkinson's disease
https://movementdisorders.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mdc3.13414
https://www.michaeljfox.org/news/mjff-survey-results-people-parkinsons-share-experiences-cannabis
2021: A review of patient charts suggest benefits for Parkinson’s disease & Lewy body dementia from the use of CBD or CBD/CBG extracts
Standardized extracts enriched in cannabidiol and cannabigerol: Real-world experience of cases series of Parkinson's disease and dementia with Lewy bodies
2021: In this case study of a man with Parkinson’s disease (which is treated by drugs that raise dopamine levels), his secret ingestion of cannabis led to intense visual hallucinations & worsening tremors
Cannabis Dopaminergic Effects Induce Hallucinations in a Patient with Parkinson’s Disease
https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/57/10/1107
2021: A survey from the Michael J Fox Foundation confirms that patients with Parkinson's often turn to cannabis
https://www.michaeljfox.org/news/fox-insight-survey-sheds-light-cannabis-use-and-parkinsons
2021: In humans, CBD well-tolerated by patients with Parkinson disease
Tolerability and Efficacy of Cannabidiol on Motor Symptoms in Parkinson Disease: Interim Report on Tolerability
https://n.neurology.org/content/96/15_Supplement/1592.abstract
2021: In humans with REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD - a common symptom of Parkinson's), CBD helped with sleep satisfaction but not to lessen manifestations of RBD
Cannabidiol for Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33754375/
2021: In humans with Parkinson's, isolated CBD decreased symptoms in half those treated (15 participants in an open label, dose escalation study)
Safety and Tolerability of Cannabidiol in Parkinson Disease: An Open Label, Dose-Escalation Study
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33381646/
2020: This survey of Parkinson's patients finds that they find cannabis helpful
Cannabis in Parkinson’s Disease: The Patients’ View
https://content.iospress.com/articles/journal-of-parkinsons-disease/jpd202260
2020: In patients with Parkinson’s disease, nabilone (a synthetic pharmaceutical THC derivative) helped with anxiety & sleep problems
Non-Motor Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease are Reduced by Nabilone
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32757413
2020: In humans with Parkinson’s disease, nabilone (synthetic THC) helped with anxiety & sleep (47 participants in a phase II placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group, enriched enrollment randomized withdrawal trial)
Non-Motor Symptoms in Parkinson's Disease are Reduced by Nabilone
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32757413/
2020: In a study of humans with Parkinson's, high levels of isolated CBD (Epidiolex) helped with their symptoms, caused no serious side effects but did elevate the liver enzymes
Safety and Tolerability of Cannabidiol in Parkinson Disease: An Open Label, Dose-Escalation Study
https://www.liebertpub.com/doi/abs/10.1089/can.2019.0068
2020: In a double-blind study of humans with Parkinson’s, 300 mg of CBD decreased anxiety and tremors during a simulation of public speaking
Effects of acute cannabidiol administration on anxiety and tremors induced by a Simulated Public Speaking Test in patients with Parkinson's disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31909680
2015: In humans with Parkinson’s disease, CB2 levels are elevated “in microglial cells recruited and activated at lesioned sites in the substantia nigra”
Potential of the cannabinoid CB(2) receptor as a pharmacological target against inflammation in Parkinson's disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25863279/
2015: A survey of cannabis use by Parkinson’s disease patients finds it effective
Self-reported efficacy of cannabis and other complementary medicine modalities by Parkinson's disease patients in Colorado
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25821504
2014: In humans with Parkinson’s disease, study finds cannabis helpful for sleep and pain (22 patients in open-label observational study)
Cannabis (medical marijuana) treatment for motor and non-motor symptoms of Parkinson disease: an open-label observational study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24614667
2014: In humans with Parkinson’s disease, CBD helped with quality of life with no significant downsides
Effects of cannabidiol in the treatment of patients with Parkinson's disease: an exploratory double-blind trial
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25237116
2014: In humans with Parkinson’s disease, CBD helped with sleep and to decrease REM sleep behavior disorder
Cannabidiol can improve complex sleep-related behaviours associated with rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder in Parkinson's disease patients: a case series
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/24845114
2009: In an open human trial, a flexible oral dose of CBD (from 150 mg to 400 mg per day) showed less psychotic symptoms, no negative effect on cognitive and motor skills and no serious side effects
Cannabidiol for the treatment of psychosis in Parkinson's disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18801821
2005: In humans with untreated Parkinson’s disease, high endocannabinoid levels found in their cerebrospinal fluid
High endogenous cannabinoid levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of untreated Parkinson's disease patients
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15852389
2004: “Anonymous questionnaire sent to all patients attending the Prague Movement Disorder Centre revealed that 25% of 339 respondents had taken cannabis and 45.9% of these described some form of benefit”
Survey on cannabis use in Parkinson's disease: subjective improvement of motor symptoms
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15372606
2004: In a case study, THC helped with musician’s dystonia
Delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol improves motor control in a patient with musician's dystonia
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15300675/
2001: In humans, CB1 agonist “significantly reduces levodopa-induced dyskinesia in PD”
Cannabinoids reduce levodopa-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease: a pilot study
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11739835
1990: In humans, letter on the history of cannabis for Parkinson’s disease tremors and 5 case studies
Marijuana for parkinsonian tremor
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC488064/
1986: In a clinical study humans with dystonia, CBD caused all 5 of them to see improvements
Open label evaluation of cannabidiol in dystonic movement disorders
Chart gallery
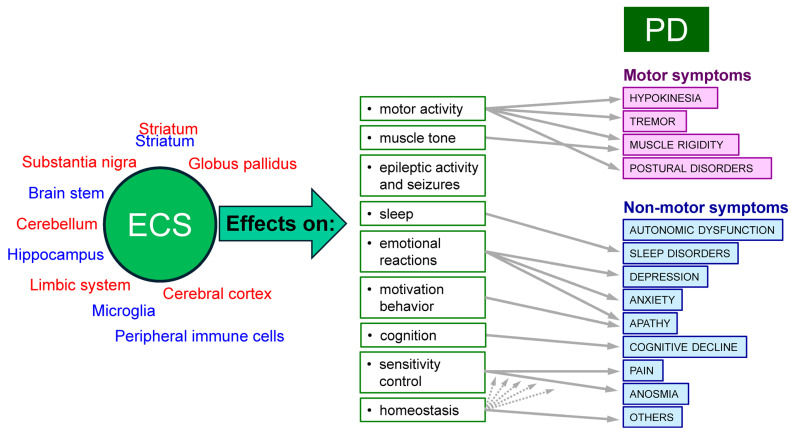
Therapeutic Application of Modulators of Endogenous Cannabinoid System in Parkinson's Disease

Cannabidiol as a Therapeutic Target: Evidence of its Neuroprotective and Neuromodulatory Function in Parkinson's Disease

The endocannabinoid system in Parkinson's disease

Therapeutic Application of Modulators of Endogenous Cannabinoid System in Parkinson's Disease
Best reviews
2024: A review of CBD for Parkinson's disease (one good chart)
CBD’s potential impact on Parkinson’s disease: An updated overview
https://digital.zlb.de/viewer/metadata/1346400695/1/
2024: For the pain of Parkinson's disease, a review of the interactions between the endocannabinoids & dopamine in the basal ganglia (good chart)
Interplay between endocannabinoids and dopamine in the basal ganglia: implications for pain in Parkinson's disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38745258/
2024: A review of using cannabinoids to treat Parkinson's disease & cancer (2 charts)
Cannabinoids in the treatment of Parkinson’s Disease and Cancer: An updated review
2024: A review of using CBD & the other cannabinoids for epilepsy MS, & Parkinson's disease as well as the psychiatric disorders that go with them (good charts)
Therapeutic applicability of cannabidiol and other phytocannabinoids in epilepsy, multiple sclerosis and Parkinson's disease and in comorbidity with psychiatric disorders
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38477419/
2024: For Parkinson's disease, a review of using THC & CBD
Current options for cannabinoids in the treatment of Parkinson's disease
https://apcz.umk.pl/QS/article/view/52922
2024: For Parkinson's disease, a review of the mechanisms CBD uses to help
The Therapeutic Potential of Cannabidiol in Parkinson's Disease: A Review of Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Effects
2024: For Parkinson’s disease, a review of cannabis use indicated “that cannabis can mitigate levodopa-induced dyskinesias and improve overall quality of life in patients”
Effects of Cannabis in Parkinson's Disease and Other Movement Disorders
2024: For Parkinson's disease, a review of how to target the endocannabinoid system (with one great chart!)
Therapeutic Application of Modulators of Endogenous Cannabinoid System in Parkinson's Disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39126088/
2024: For Parkinson's disease, a review of the neuroprotective effects via the endocannabinoid system
Potential Neuroprotective Effect of the Endocannabinoid System on Parkinson's Disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39104613/
2023: For Parkinson's disease, a review of 13 studies on using THC & CBD
Cannabinoids in Treating Parkinson's Disease Symptoms: A Systematic Review of Clinical Studies
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37253174/
2023: For Parkinson's disease, a review of 95 articles on the use of cannabinoids
Beyond conventional therapy: cannabinoids as an alternative in parkinson's disease
https://ojs.observatoriolatinoamericano.com/ojs/index.php/olel/article/view/2313
2021: This review looks at 18 studies showing how cannabinoids & resveratrol help with neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease
The Neuroprotective Effects of Cannabis-Derived Phytocannabinoids and Resveratrol in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Literature Review of Pre-Clinical Studies
https://www.mdpi.com/2076-3425/11/12/1573
2021: A review of the use of oral cannabinoids for seborrheic dermatitis - a common skin issue among Parkinson's disease patients
A Review of the Current Evidence Connecting Seborrheic Dermatitis and Parkinson’s Disease and the Potential Role of Oral Cannabinoids
https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/512189
2020: How the relationship between the ECS and the microglia (immune cells of the brain) could benefit Parkinson's patients
Microglial Phenotypes and Their Relationship to the Cannabinoid System: Therapeutic Implications for Parkinson's Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31973235
2020: For Parkinson's disease, this intriguing review looks at complementary therapies to go along with dopamine replacement including acupuncture, tai chi, qi gong, & cannabis
Complementary Therapies in Parkinson Disease: a Review of Acupuncture, Tai Chi, Qi Gong, Yoga, and Cannabis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32785848/
2019: CBD & the cannabinoids for the L-DOPA dyskinesia
Cannabidiol and Cannabinoid Compounds as Potential Strategies for Treating Parkinson's Disease and L-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31637586
Timeline of Research
2025: In a rat model of Parkinson's, both CBD pre-administration & CBD treatment reduced motor alterations & lessened catalepsy
Preventive Beneficial Effects of Cannabidiol in a Reserpine-Induced Progressive Model of Parkinsonism
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/pharmacology/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1539783/abstract
2025: In a mouse model of Parkinson's, the terpene beta-caryophyllene reduced blood-brain permeability & loss of dopamine-producing neurons via the CB2 receptor
Beta-Caryophyllene Inhibits the Permeability of the Blood-Brain Barrier in MPTP-Induced Parkinsonism
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40054982/
2025: In a mouse model of Parkinson's, exercise training improved their motor performance & learning skills via expression levels of the CB1 receptor
The Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Mediates Exercise-Induced Improvements of Motor Skill Learning and Performance in Parkinsonian Mouse
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0014488625001530
2025: In a mouse model of Parkinson's disease, activation of the CB2 receptor not only decreased inflammation but also formed receptor heteromers (joined receptor units) with NMDA glutamate receptors to lessen their detrimental increased signaling
The interplay between CB2 and NMDA receptors in Parkinson’s disease
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.01.20.633878v1.full.pdf
2025: In a mouse model of Parkinson's disease, activation of the CB2 receptor was necessary for the neuroprotective effects (though not on the peripheral immune cells)
Activation of central cannabinoid type 2 receptors, but not on peripheral immune cells, is required for endocannabinoid-mediated neuroprotection in Parkinson's disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40320016/
2024: In a rat model of Parkinson's disease, CBD improved symptoms and helped newborn neurons
Cannabidiol improves nonmotor symptoms, attenuates neuroinflammation and favors hippocampal newborn neuronal maturation in a rat model of Parkinsonism
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38770713/
2024: In a rat model of dyskinesia from the levodopa treatment of Parkinson's disease, cannabinoids reduced the calcium dyshomeostasis & led to a partial recovery
Cannabinoid regulation of angiotensin II-induced calcium signaling in striatal neurons
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41531-024-00827-7
2024: In a rat model of diabetic Parkinson's disease, CBD nanoparticles lessened metabolic & memory impairments via the modulation of dopamine levels & changes to the hippocampus (memory center of the brain)
Assessing the Safety and Therapeutic Efficacy of Cannabidiol Lipid Nanoparticles in Alleviating Metabolic and Memory Impairments and Hippocampal Histopathological Changes in Diabetic Parkinson's Rats
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38675175/
2024: In a model of Parkinson's disease, the terpene beta-caryophyllene decreased neuroinflammation & caused neuroprotection of the dopamine-producing neurons
β-Caryophyllene decreases neuroinflammation and exerts neuroprotection of dopaminergic neurons in a model of hemiparkinsonism through inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome
https://www.prd-journal.com/article/S1353-8020(24)00834-4/abstract
2024: In a tissue model of Parkinson's disease, the terpenes linalool & geraniol protected the neurons from oxidative stress & inflammation as well as from increased levels of iron
Linalool and Geraniol Defend Neurons from Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Iron Accumulation in In Vitro Parkinson’s Models
2024: In a mouse model of Parkinson's, the phenylpropionamides of cannabis seeds improved behavioral symptoms, probably via the regulation of autophagy (cellular recycling)
Protective effect of phenylpropionamides in the seed of Cannabis Sativa L. on Parkinson's disease through autophagy
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38458497/
2024: In a mouse model of Parkinson's disease, hemp seed peptides reduced neural protein aggregates & lowered inflammatory gene expression
Immunomodulatory properties of hempseed oligopeptides in an LRRK2-associated Parkinson's disease animal model
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39435853/
2024: In a mouse model of the dyskinesia from the Parkinson's treatment drug L-DOPA, a CBD derivative combined with a drug to activate the CB2 receptor (HU-910) decreased their dyskinesia & normalized their glutamate
4'-fluorocannabidiol associated with capsazepine restrains L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in hemiparkinsonian mice: Contribution of anti-inflammatory and anti-glutamatergic mechanisms
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38554815/
2024: In a mouse model of Parkinson's disease, the CBG derivative VCE-003.2 improved performance in motor tests, preserved neurons & reduced reactive microgliosis & astrogliosis (abnormally strong reactions from the microglia & astrocytes respectively)
Investigation in the cannabigerol derivative VCE-003.2 as a disease-modifying agent in a mouse model of experimental synucleinopathy
https://behavioralandbrainfunctions.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12993-024-00256-9
2024: In a rat model of Parkinson's disease, the synthetic cannabinoid JWH133 (which activates CB2) improved their behaviors & protected dopamine-producing neurons
JWH133 attenuates behavior deficits and iron accumulation in 6-OHDA-induced Parkinson's disease model rats
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39015077/
2024: In a rat model of Parkinson's disease, activating the CB2 receptor delayed immune cell infiltration into the brain, decreased pro-inflammatory white blood cells & elevated wound healing white blood cells & wound-healing gene expression
Modulation of cannabinoid receptor 2 alters neuroinflammation and reduces formation of alpha-synuclein aggregates in a rat model of nigral synucleinopathy
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39334169/
2024: In a mouse model of Parkinson's disease, they had fewer complexes of CB1 receptors joined to NMDA receptors (glutamate, the brain’s most common excitatory neurotransmitter)
The Expression and Functionality of CB1R-NMDAR Complexes Are Decreased in A Parkinson's Disease Model
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38474266/
2024: For Parkinson's disease, the treatment effects of the drugs xanthine or hypoxanthine may be mediated by the endocannabinoid system via GABA
Xanthine or hypoxanthine or both may play therapeutical effect in Parkinson's disease through the endocannabinoid system
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S030698772300227X
2024: For Parkinson's disease, a thesis project on using roundworms as a model to determine the effectiveness of CBD as a treatment
Cannabinoids and Neurodegeneration: Using C. elegans as a Model System to Determine the Effectiveness of CBD as a Treatment for Parkinson’s Disease
https://digital.wpi.edu/concern/student_works/z603r2859?locale=fr
2023: In a rat model of Parkinson's disease, chronic cannabis administration decreased CB1 levels, increased CB2 levels & may be helpful for learning & memory disorders via the dopamine & cannabinoid receptors
The Effects of Chronic Marijuana Administration on 6-OHDA-Induced Learning & Memory Impairment and Hippocampal Dopamine and Cannabinoid Receptors Interaction in Male Rats
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36894794/
2023: In a rat model of Parkinson's disease, CBD & CBG - whether given separately or together - decreased L-DOPA medication’s dyskinesia (involuntary erratic movements caused by high dopamine levels)
CANNABIDIOL AND CANNABIGEROL LIMIT L-DOPA-INDUCED DYSKINESIA WHEN GIVEN SEPARATELY OR IN COMBINATION TO HEMIPARKINSONIAN RATS
https://www.ibroneuroreports.org/article/S2667-2421(23)00737-6/fulltext
2023: In a fish model of Parkinson’s disease, CBD almost completely reversed the motor dysfunction via dopamine receptors & did so better than a common treatment drug
Cannabidiol improves haloperidol-induced motor dysfunction in zebrafish: a comparative study with a dopamine activating drug
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36871008/
2023: In a roundworm model of Parkinson's disease, CBD rescued damage to the dopamine producing neurons
Cannabidiol Recovers Dopaminergic Neuronal Damage Induced by Reserpine or α-synuclein in Caenorhabditis elegans
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36964823/
2023: In a tissue model of Parkinson's disease, CBN caused changes to gene expression that helped to protect the mitochondria (powerhouse of the cell)
Transcriptome Highlights Cannabinol Modulation of Mitophagy in a Parkinson's Disease In Vitro Model
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37627228/
2023: A thesis project on the neuroprotective effects of cannabis extracts in a model of Parkinson's disease
In vivo Neuroprotective Effects of Cannabis sativa in Models of Parkinson’s Disease
2023: In a mouse model of Parkinson's disease, a CBG derivative improved their neurological status & preserved neurons
The Cannabigerol Derivative VCE-003.2 Exerts Therapeutic Effects in 6-Hydroxydopamine-Lesioned Mice: Comparison with The Classic Dopaminergic Replacement Therapy
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37759872/
2023: In an animal model of Parkinson's disease, the terpene beta caryophyllene decreased neuroinflammation & protected the dopamine neurons via inhibition of the inflammasome
β-Caryophyllene decreases neuroinflammation and exerts neuroprotection of dopaminergic neurons in a model of hemiparkinsonism through inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37924806/
2023: In a rat model of Parkinson's disease, exercise on a treadmill increased CB1 levels in the hippocampus & substantia nigra with a suggested beneficial effect on pain
Treadmill exercise modulates nigral and hippocampal cannabinoid receptor type 1 in the 6-OHDA model of Parkinson's disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37268248/
2023: In a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, activating the CB2 receptor lowered the inflammation & dopamine neuron loss via the PI3K/Akt pathway
Activation of cannabinoid receptor 2 inhibits LPS-induced neuroinflammation via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in mice
2023: In a mouse model of Parkinson's, targeting the CB2 receptors of the astrocytes protected motor abilities, lowered neuroinflammation & lessened disease characteristics via the NLRP3/Caspase-1/IL-1β pathway & inhibition of foxg1 binding to MAP1LC3B
Targeting CB2R in astrocytes for Parkinson's disease therapy: unraveling the Foxg1-mediated neuroprotective mechanism through autophagy-mediated NLRP3 degradation
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38110963/
2023: In microglial cells (guardian immune cells of the brain) that model Parkinson's disease, activation of the CB2 receptor inhibited their inflammatory state
Cannabinoid type 2 receptor activation inhibits MPP+-induced M1 differentiation of microglia through activating PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 signal pathway
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36977807/
2023: A machine learning analysis of available drugs suggests the use of THC for Parkinson's disease
Machine learning study: from the toxicity studies to tetrahydrocannabinol effects on Parkinson's disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36942739/
2023: On designing Parkinson's disease drugs based on cannabinoids
Design of Cannabinoid-Based Drugs for the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-031-46545-1_22
2022: In a rat model of tardive dyskinesia (repetitive movement of facial muscles), CBD helped the standard treatment of haloperidol to work better
The effects of cannabidiol on behavioural and oxidative stress parameters induced by prolonged haloperidol administration
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36328984
2022: In a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, CBD improved cognitive dysfunction & increased locomotion, decreased neuroinflammation & protected the dopamine producing neurons
Cannabidiol Alleviates the Damage to Dopaminergic Neurons in 1-Methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-Tetrahydropyridine-Induced Parkinson's Disease Mice Via Regulating Neuronal Apoptosis and Neuroinflammation
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35792194
2022: In a mouse model of Parkinson’s, CBD significantly improved motor deficits & protected the midbrain via the gut-brain axis
Effects of Cannabidiol on Parkinson's Disease in a Transgenic Mouse Model by Gut-Brain Metabolic Analysis
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35360659/
2022: In a rat model of Parkinson’s disease, injection of CBD into the brain improved their fine motor skills via the GPR55 receptor & GABA
Intrapallidal injection of cannabidiol or a selective GPR55 antagonist decreases motor asymmetry and improves fine motor skills in hemiparkinsonian rats
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36120297
2022: In a roundworm model of Parkinson’s, CBD protected the neurons that produce dopamine, decreased their food-sensing disabilities, reduced oxidation & increased their lifespan
Neuroprotective effects of cannabidiol on dopaminergic neurodegeneration and α-synuclein accumulation in C. elegans models of Parkinson's disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36108815
2022: In a roundworm model of Parkinson’s disease, CBDV lowered the aggregation of the α-synuclein plaques as well as oxidative stress & the death of dopamine producing neurons
Cannabidivarin alleviates α-synuclein aggregation via DAF-16 in Caenorhabditis elegans
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36583706/
2022: In α-synucleinopathy (the buildup of α-synuclein in neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s & dementia with Lewy bodies), the CB2 receptor is critical for the necessary synaptic pruning by the microglia (guardian cells of the brain)
Loss of cannabinoid receptor 2 promotes α-Synuclein-induced microglial synaptic pruning in nucleus accumbens by modulating the pCREB-c-Fos signaling pathway and complement system
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36162511
2022: In a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, activating the CB2 receptor reduced their anxious & depressive behaviors & improved motor deficits
CB2 Agonist GW842166x Protected against 6-OHDA-Induced Anxiogenic- and Depressive-Related Behaviors in Mice
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35892676
2022: In a mouse model of Parkinson’s, not having enough DAGLB (the enzyme that creates the endocannabinoid 2-AG) caused impaired locomotor skill learning & worse disease progression, suggesting increased 2-AG as a treatment
Deficiency in endocannabinoid synthase DAGLB contributes to early onset Parkinsonism and murine nigral dopaminergic neuron dysfunction
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35715418
2022: A protein analysis of pathways finds that endocannabinoids are involved in the dysregulation produced by Parkinson’s disease
Mass Spectrometry-Based Proteomics Analysis of Human Substantia Nigra From Parkinson's Disease Patients Identifies Multiple Pathways Potentially Involved in the Disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36423813
2022: In a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, activating the CB2 receptor reduced their anxious & depressive behaviors & improved motor deficits
CB2 Agonist GW842166x Protected against 6-OHDA-Induced Anxiogenic- and Depressive-Related Behaviors in Mice
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35892676
2022: In a rat model of Parkinson’s, this research looks at how the endocannabinoidome is altered by the α-synuclein of the disease
Time-Course of Alterations in the Endocannabinoid System after Viral-Mediated Overexpression of α-Synuclein in the Rat Brain
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35056822/
2022: In a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, an activator of the CB2 receptor is neuroprotective
The Neuroprotective Effects of the CB2 Agonist GW842166x in the 6-OHDA Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34944056/
2022: In a rat model of Parkinson’s disease, a combination of a CB1 blocker along with the standard treatment of L-DOPA helped to protect the dopamine neurons as well as alleviating motor symptoms
L-DOPA/Capsazepine or L-DOPA/Rimonabant Co-Administration in an Experimental Parkinson Disease Model: Behavioral and Cellular Consequences
https://stm.bookpi.org/IDMMR-V5/article/view/5580
2022: In a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, targeting the NAAA enzyme (which breaks down PEA) protects from dopamine neuron loss & parkinsonian symptoms
Targeting NAAA counters dopamine neuron loss and symptom progression in mouse models of Parkinson’s disease
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.02.10.479850v1.full.pdf
2022: In an animal model of Parkinson’s disease, treatment with CBD caused less neural degeneration, less neuroinflammation & an improvement in motor performance
Neuroprotective and Symptomatic Effects of Cannabidiol in an Animal Model of Parkinson's Disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34445626/
2021: In a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, the combination of exercise & a FAAH inhibitor (a function of CBD) had a positive effect on all parameters measured
The effect of URB597, exercise or their combination on the performance of 6-OHDA mouse model of Parkinson disease in the elevated plus maze, tail suspension test and step-down task
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34599739/
2021: In an animal model of Parkinson’s disease, CBD acted as both a neuroprotective as well an agent to treat the symptoms
Neuroprotective and Symptomatic Effects of Cannabidiol in an Animal Model of Parkinson's Disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34445626/
2021: In a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease, THC protected the dopamine producing neurons by antioxidant effects, decreasing cell death & protecting the mitochondria (powerhouse of the cell)
Neuroprotective Effects of Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol against FeSO4- and H2O2-Induced Cell Damage on Dopaminergic Neurons in Primary Mesencephalic Cell Culture
https://www.thieme-connect.com/products/ejournals/html/10.1055/a-1516-4182
2021: In a rat model of Parkinson’s, cannabis improved their motor control via an increase in synaptic plasticity
Marijuana improved motor impairments and changes in synaptic plasticity-related molecules in the striatum in 6-OHDA-treated rats
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33961911
2021: In mice, the brain’s medium spiny neurons – which contain the highest levels of CB1 receptors in the CNS – control exploration & motor coordination partially via the ECS
Control of exploration, motor coordination and amphetamine sensitization by cannabinoid CB 1 receptors expressed in medium spiny neurons
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34216157/
2021: In a rat model of Parkinson’s disease, CBD helped with their musculoskeletal pain
Cannabidiol has therapeutic potential for myofascial pain in female and male parkinsonian rats
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34246682/
2021: In rats, they found that the endocannabinoid system plays a major role in the globus pallidus (a brain region important for movement)
In vivo bidirectional modulation of cannabinoid on the activity of globus pallidus in rats
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34129911/
2021: In mice with a movement disorder, CBD helped to alleviate the facial tics from the treatment drug haloperidol as well as lowering proinflammatory cytokines in the striatum & hippocampus of the brain via the PPARγ nuclear receptors
PPARγ receptors are involved in the effects of cannabidiol on orofacial dyskinesia and cognitive dysfunction induced by typical antipsychotic in mice
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34048863/
2021: In a neural model of Parkinson's, CBD acts as a protector of neurons, especially from the dysfunctions of the mitochondria (the powerhouse of the cell)
Cannabidiol Induces Autophagy to Protects Neural Cells From Mitochondrial Dysfunction by Upregulating SIRT1 to Inhibits NF-κB and NOTCH Pathways
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fncel.2021.654340/full
2021: In a cellular model of Parkinson's disease, activation of the CB1 receptor lowered stress & inflammation
Cannabinoid receptor-1 has an effect on CD200 under rotenone and alpha-synuclein induced stress
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S030439402100286X
2021: In rats, the protection of paracetamol against Parkinson's disease may be mediated by the endocannabinoid system
Mechanistic insights into the protective effect of paracetamol against rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease in rats: Possible role of endocannabinoid system modulation
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1567576921000679
2021: In neurons, the loss of dopamine harms the ability of the CB1 receptors to operate (perhaps explaining some of the symptoms of Parkinson's disease)
Dopaminergic denervation impairs cortical motor and associative/limbic information processing through the basal ganglia and its modulation by the CB1 receptor
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33278598/
2020: In a mouse model of tardive dyskinesia, CBD prevented microglial activation & prevented neuroinflammation via PPARγ
Cannabidiol prevents haloperidol-induced vacuos chewing movements and inflammatory changes in mice via PPARγ receptors
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30217539/
2020: In the brains of monkeys with induced parkinsonism, complexes of CB1+GPR55 and CB2+GPR55 appear to be targets for treating Parkinson's
Expression of GPR55 and either cannabinoid CB 1 or CB 2 heteroreceptor complexes in the caudate, putamen, and accumbens nuclei of control, parkinsonian, and dyskinetic non-human primates
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32691218/
2020: In mice with Parkinson's, THCV helped with the dyskinesia resulting from L-DOPA treatment
Beneficial effects of the phytocannabinoid Δ 9-THCV in L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in Parkinson's disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32387338/
2020: In a cellular model of Parkinson's disease, CBD caused a wide array of positive effects via the AKT/mTOR pathway
Cannabidiol exerts protective effects in an in vitro model of Parkinson's disease activating AKT/mTOR pathway
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32184097
2019: In an animal model of Parkinson's, CBD increases the pain threshold
Cannabidiol increases the nociceptive threshold in a preclinical model of Parkinson's disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31706993/
2019: In a mouse model of dyskinesia, activation of the CB2 receptor may reduce symptoms
Targeting the cannabinoid receptor CB2 in a mouse model of l-dopa induced dyskinesia
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31669673
2018: In postmortem human brains, CB1, CB2 & MAGL found to be closely related to the neuropathological processes of PD
Cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 Receptors, and Monoacylglycerol Lipase Gene Expression Alterations in the Basal Ganglia of Patients with Parkinson's Disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29352424/
2016: In rats, CBD prevented the impairments of reserpine (used for high blood pressure & psychotic symptoms)
Cannabidiol Prevents Motor and Cognitive Impairments Induced by Reserpine in Rats
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27733830
2015: In tissue culture, CBD protected against a model of Parkinson’s disease via several neuronal proteins
The neuroprotection of cannabidiol against MPP⁺-induced toxicity in PC12 cells involves trkA receptors, upregulation of axonal and synaptic proteins, neuritogenesis, and might be relevant to Parkinson's disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26556726/
2014: In rat model of Parkinson’s disease, a CB1 antagonist and an adenosine antagonist worked to protect dopaminergic neuron cell death – but did worse when combined together
Neuroprotective potential of adenosine A2A and cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonists in an animal model of Parkinson disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24709676/
2013: In rats, CBD influenced vertical motor activity – probably via serotonin
Motor effects of the non-psychotropic phytocannabinoid cannabidiol that are mediated by 5-HT1A receptors
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23924692/
2013: In mice, CBD attenuates drug-induced catalepsy from Parkinsons's treatment via serotonin
Cannabidiol attenuates catalepsy induced by distinct pharmacological mechanisms via 5-HT1A receptor activation in mice
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23791616
2012: In cell culture, THC causes direct neuroprotective effect against PD – may be mediated via PPARγ
Δ⁹-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ⁹-THC) exerts a direct neuroprotective effect in a human cell culture model of Parkinson's disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22236282
2011: In a rat model of Parkinson’s disease, THCV neuroprotective and symptom relieving
Symptom-relieving and neuroprotective effects of the phytocannabinoid Δ9-THCV in animal models of Parkinson's disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21323909
2011: In a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease, MAGL inhibition to combat neuroinflammation
Endocannabinoid hydrolysis generates brain prostaglandins that promote neuroinflammation
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22021672
2010: In rats, blockade of CB1 suggested for early disease symptoms of PD
Effects of SR141716A on Cognitive and Depression-Related Behavior in an Animal Model of Premotor Parkinson's Disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2957172/
2009: In rats, Rimonabant improved PD by itself and in addition to regular therapy
The CB(1) antagonist rimonabant is adjunctively therapeutic as well as monotherapeutic in an animal model of Parkinson's disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19414037
2009: In rats, a cannabinoid agonist helps with dyskinesia via changes in dopamine and glutamate
Neurochemical changes in the striatum of dyskinetic rats after administration of the cannabinoid agonist WIN55,212-2
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19010365
2009: In rats, CB2 agonism suggested to slow progress of Parkinson’s disease
WIN55,212-2, a cannabinoid receptor agonist, protects against nigrostriatal cell loss in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine mouse model of Parkinson's disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19490092
2008: In rat model of Parkinson’s disease, activating 5HT1A (as CBD does) reduces dopamine D1 dyskinesia
Striatal 5-HT1A receptor stimulation reduces D1 receptor-induced dyskinesia and improves movement in the hemiparkinsonian rat
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18824001
2008: In flies, a CB1/CB2 agonist protects against paraquat neurotoxicity and its antioxidant properties suggest cannabinoids for Parkinson’s disease
The cannabinoid CP55,940 prolongs survival and improves locomotor activity in Drosophila melanogaster against paraquat: implications in Parkinson's disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18538428
2007: In an animal model of Parkinson’s disease, the ECS helps to rescue motor skills & striatal long-term depression
Endocannabinoid-mediated rescue of striatal LTD and motor deficits in Parkinson's disease models
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17287809/
2007: In a rat model of Parkinson’s disease, tested an array of cannabinoids and found their help was independent of CB1 & CB2 receptors – but CB2 activation may also be helpful – upregulated the Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase antioxidant machinery
Evaluation of the neuroprotective effect of cannabinoids in a rat model of Parkinson's disease: importance of antioxidant and cannabinoid receptor-independent properties
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17196181/
2007: In primates, CB1 antagonists seem to levodopa work better for Parkinson’s disease
Blockade of cannabinoid type 1 receptors augments the antiparkinsonian action of levodopa without affecting dyskinesias in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-treated rhesus monkeys
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17630359
2007: In rats, on how CB1 & TRPV1 interact with levodopa for Parkinson’s disease
Anti-dyskinetic effects of cannabinoids in a rat model of Parkinson's disease: role of CB(1) and TRPV1 receptors
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17900568
2006: In rats, Rimonabant seems effective for Parkinson’s disease at low doses but effect not related to dopaminergic, GABAergic, or glutamatergic transmission in the striatum
Effects of rimonabant, a selective cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist, in a rat model of Parkinson's disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16412990
2005: In a tissue & animal model of Parkinson’s disease, the neuroprotective properties of cannabinoids
Cannabinoids provide neuroprotection against 6-hydroxydopamine toxicity in vivo and in vitro: relevance to Parkinson's disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15837565
2005: In rats, CB1 antagonists seem to only be effective in late stage Parkinson’s disease
Cannabinoid CB1 antagonists possess antiparkinsonian efficacy only in rats with very severe nigral lesion in experimental parkinsonism
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15755685
2005: In primates, the potential roles of CB1 and the endocannabinoids for Parkinson’s disease
A role for endocannabinoids in the generation of parkinsonism and levodopa-induced dyskinesia in MPTP-lesioned non-human primate models of Parkinson's disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15894565
2002: In primates, cannabinoid receptor agonists reduces the dyskinesia of levodopa
Stimulation of cannabinoid receptors reduces levodopa-induced dyskinesia in the MPTP-lesioned nonhuman primate model of Parkinson's disease
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12465055
2002: In a hamster model of dyskinesia, WIN 55,212-2 helped but seemingly not by the CB1 receptor
Effects of pharmacological manipulations of cannabinoid receptors on severity of dystonia in a genetic model of paroxysmal dyskinesia
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12421641/
1998: In rats, the effects of cannabinoids in the basal ganglia
Cannabinoid effects in basal ganglia in a rat model of Parkinson's disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9654336/